Inhibiting Factors of the Acceleration of Irrigation Water Use Improvement Program
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v12i1.721Keywords:
P3-TGAI, Community assistant, Inhibiting factorsAbstract
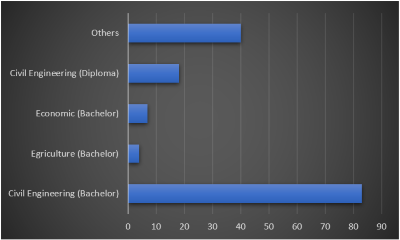
Inhibiting Factors of the Acceleration of Irrigation Water Use Improvement Program (P3-TGAI) is a program for rehabilitation, improvement, or construction of irrigation networks based on the participation of farming communities which is carried out in a self-managed or non-contractual manner follow-up to the Ministry of PUPR Directorate General of Water Resources. Based on the evaluation results from Pambudi & Pramujo in 2023, the implementation of P3-TGAI activities at the basic level still encounters various problems, although in general many successes have been achieved. These problems are seen from the aspects of funding transparency, institutional readiness in the field, late determination of target locations, and less than optimal socialization at the farm level. These problems will hamper the aims, objectives, and goals of P3-TGAI activities. In order for the future implementation of this activity to run smoothly, research was conducted to find out what are the inhibiting factors that have the potential to hinder the success of this inhibiting activity in the preparation stage, planning stage, and implementation stage. The research was conducted using a quantitative descriptive method with a questionnaire instrument. The questionnaire was distributed to assistants. From the results of the study, it was found that there were 15 inhibiting factors with a very high influence on the implementation of P3-TGAI activities. 60% of them came from the preparation stage, 27% came from the implementation stage, and the rest (13.3%) came from the planning stage. Of all the inhibiting factors with a very high influence, there is one inhibiting factor with the highest score, namely communication with the community is not good. The solution to poor communication with the community is that the assistants build good emotional relationships with the community, ТPM must often go to the field, and assistants mingle with the community. In terms of general project objectives, inhibiting factors that hinder timeliness are lack of community participation and poor communication and coordination by the community. The inhibiting factors that hinder quality accuracy are the lack of knowledge and experience of the assistants and the lack of socialization to the village community. And the inhibiting factor that hinders cost accuracy is that the community is manipulated by other parties.
Downloads
References
Y. Singgalen, G. Sasongko, and P. Wiloso, “Community Participation in Regional Tourism Development: A Case Study in North Halmahera Regency-Indonesia,” Insight Into Regional Development, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 318–333, 2019.
S. Hajar, “Pembangunan Berbasis Pemberdayaan Masyarakat,” Jurnal Sosial Humaniora dan Komunikasi, pp. 248–252, 2020.
Kementerian PUPR, “Permen PUPR Nomor 4 Tahun 2021 tentang Program Percepatan Peningkatan Tata Guna Air Irigasi,” 2021, Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat, Jakarta.
Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional, “Rencana Pembangunan Jangka Menengah Nasional,” 2019, Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Nasional, Jakarta.
D. M. Adji, B. Istijono, T. Ophiyandri, B. Hidayat, and M. Rahendra, “The Implementation of Health Protocol in Irrigation Small Scale Project in Padang Pariaman District,” International Journal on Advanced Science Engineering Information Technology, pp. 1463–1471, 2023.
B. Hidayat et al., “Analysis of the government regulations on COVID-19 pandemics in Indonesia: implementation and challenges,” E3S Web of Conferences, vol. 331, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202133101016.
Balai Wilayah Sungai Sumatera V, Petunjuk Pelaksanaan P3-TGAI. Padang: Kementerian Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat, 2023.
F. H. Ali and A. H. S. Ali, “The Role of Irrigation Projects in The Development of Rural Settlements Conceptual Framework and Experiences,” 3rd Internatioanl Conference on Smart Cities and Sustainable Palnning, no. 1129, pp. 1–11, 2023.
A. S. Pambudi and B. Pramujo, “Evaluasi Pengembangan Program Percepatan Peningkatan Tata Guna Air Irigasi (P3-TGAI) di Masa Pandemi Covid-19,” in Pertemuan Ilmiah Tahunan ke 40 HATHI, Bandar Lampung: Himpunan Ahli Teknik Hidrauilik Indonesia, 2023, pp. 213–225.
D. G. Eshete, B. G. Sinshaw, and K. G. Legese, “Critical review on improving irrigation water use efficiency: Advances , challenges , and opportunities in the Ethiopia context,” Water-Energy Nexus, vol. 3, pp. 143–154, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.wen.2020.09.001.
M. Thohir, A. Putranta, and A. Sudiarno, “Scheduling Optimalization of Swakelola Projects in The Irrigation Water Utilization Improvement Program (P3-TGAI),” IPTEK Journal of Proceedings Series, 2021.
Z. N. Azka and S. Hasib, “The Phenomenon Study of Effective Communication of Trainers in The Induction Training,” Journal of Advances in Humanities and Social Sciences, vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 147–155, 2020.
B. Istijono and T. Ophiyandri, “Community-Based Approach in A Small Scale Irrigation Project in Indonesia: Ways and Advantages,” Civil Engineering Dimension, pp. 95–100, 2015.
R. Samaun, B. Bakri, and A. Mediansyah, “Upaya Pemerinta Desa Mendorong Partisipasi Masyarakat Dalam Pembangunan Desa Oluhuta Kecamatan Atinggola Kabupaten Gorontalo Utara,” Jurnal Ilmu Pemerintahan dan Komunikasi, pp. 18–33.
T. Ophiyandri, D. Amaratunga, C. Pathirage, and K. Keraminiyage, “Critical success factors for community-based post-disaster housing reconstruction projects in the pre-construction stage in Indonesia,” Int J Disaster Resil Built Environ, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 236–249, Jul. 2013, doi: 10.1108/IJDRBE-03-2013-0005.
A. Dilapanga, B. Supit, and A. Mandagi, “The Role of Community Participation in Supporting Tomohon City Regional Regulation No. 1 of 2021,” in New Publlic Governance: Reflection to Administrative Science, Padang: IAPA Annual Internatioanl Conference and International Indonesia Conference on Interdisiplinary Studies (IICIS), 2023, pp. 36–36.
T. Ophiyandri, D. Amaratunga, and K. Keraminiyage, “Advantages and Limitations of Community-based Post-disaster Housing Reconstruction Projects,” Int J Disaster Resil Built Environ, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 420–431, 2016.
Y. L. Ta’dung and W. Lusdani, “Akuntabilitas Sosial Dana Desa: Peran dan Partisipasi Masyarakat,” Jurnal Ekonomi, Bisnis dan Terapan, pp. 25–33.
A. K. Biswas, “Monitoring and Evaluation of Irrigation Projects,” Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering, vol. 116, no. 2, pp. 227–242, 1990.
M. Nasution, Zulkarnaini, and H. Simanjuntak, “Collaborative Governance - Can It Achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Towards Independents Villages in Strategic Border Areas,” in New Publlic Governance: Reflection to Administrative Science, Padang: IAPA Annual Internatioanl Conference and International Indonesia Conference on Interdisiplinary Studies (IICIS), 2023, pp. 85–99.
D. Rahmawati, Y. Yuliana, Ricih, and Rusmiyati, “Implementasi Kebijakan Program Percepatan Peningkatan Tata Guna Air Irigasi (P3-TGAI) oleh Balai Besar Wilayah Sungai Sumatera VIII di Kota Palembang,” Jurnal Ilmu Administrasi dan Studi Kebijakan, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 101–116, 2022.
B. Hidayat and C. Egbu, “Critical Success Factors Associated With Post-Disaster Reconstruction Projects,” in Procs 27th Annual ARCOM Conference, Bristol, UK, Sep. 2011, pp. 889–898. [Online]. Available: www.em-dat.net
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nadia Permata, Benny Hidayat, Taufika Ophiyandri

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







2.jpg)
