Lateral Spreading in Christchurch, New Zealand: An Empirical Approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v11i3.593Keywords:
Lateral Spreading, Empirical Method, Bartlett & Youd Method (2002), Byrne Method (1990)Abstract
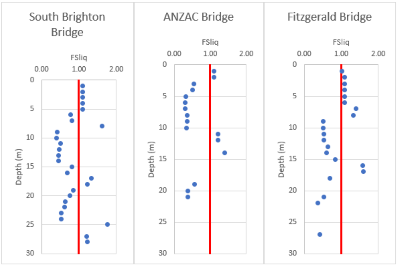
Lateral spreading, a complex phenomenon resulting from liquefaction, manifests when saturated, cohesionless soils lose their strength during seismic events, causing them to deform and flow horizontally. This process poses a substantial risk to buildings and infrastructure, often resulting in extensive damage, significant financial burdens, and, tragically, loss of life. In Indonesian, liquefaction is recognized for its ability to transform solid ground into a fluid-like state, amplifying its danger in regions prone to earthquakes. This study aims to analyze lateral spreading through empirical methods, specifically employing the Bartlett & Youd Method (2002) and the Byrne Method (1990). The analysis focuses on sites previously affected by lateral spreading, notably those impacted by the 22 February 2011 Christchurch earthquake, which registered a magnitude of 6.2 and a peak ground acceleration of 0.52. The selected locations include the South Brighton Bridge, Anzac Bridge, and Fitzgerald Bridge in Christchurch, New Zealand. The findings demonstrate that both the Bartlett & Youd Method (2002) and the Byrne Method (1990) yield results that closely approximate the actual conditions at site.
Downloads
References
M. Cubrinovski, J. Haskell, A. Winkley, K. Robinson and L. Wotherspoon, "Performance of Bridges in Liquefied Deposits during the 2010–2011 Christchurch, New Zealand, Earthquakes," JOURNAL OF PERFORMANCE OF CONSTRUCTED FACILITIES, pp. 24-39, 2014.
"Investigation Logs," CGD (Canterbury Geotechnical Database), 2012. [Online]. Available: https://www.nzgd.org.nz/. [Accessed 1 January 2024].
SNI 4135:2008, Badan Standardisasi Nasional, 2008.
J. D. B. J. M. R. L. Christopher S. Markham, "Evaluating nonlinear effective stress site response analyses using," Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 82, no. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, pp. 84-98, 2015.
C. M. H. a. S. F. B. T. Leslie Youd, "Revised Multilinear Regression Equations for Prediction," JOURNAL OF GEOTECHNICAL AND GEOENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING, pp. 1007-1017, 2002.
P. M. Byrne, "A Model for Predicting Liquefaction Induced Displacement," in 1991 - Second International Conference on Recent Advances in Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering & Soil Dynamics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, B.C., Canada, 1991.
D. M. P. T. Leslie Youd, "Mapping Liquefaction-Induced Ground Failure Potential," Journal of Geotechnical Engineering Division, pp. 433-446, 1978.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Megah Ultari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







2.jpg)
