Evaluation of TPS 3R and Waste Bank Management in Sungai Penuh City
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v11i2.548Keywords:
Household Waste, TPS 3R, Waste Bank, Evaluation, ReductionAbstract
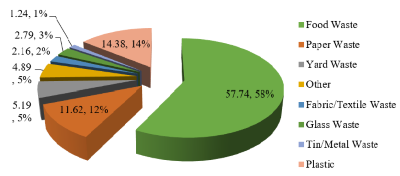
Sungai Penuh City has 16 units of TPS 3R and 1 unit of waste bank that are not operating optimally. The evaluation to determine the condition of TPS 3R and waste bank and the potential reduction obtained if they are operated again. The research began by collecting data on generation of solid waste, composition, and recycling possibilities for household waste. Sampling of waste generation based on SNI 19-3964-1994 in 8 sub-districts in Sungai Penuh City for 8 consecutive days with the household generation of solid waste outcome of 0.328 kg/person/day or 2.789 l/person/day. The composition of household waste in Sungai Penuh City includes 57.74% food waste, 14.38% plastic waste, 11.62% paper waste, 5.19% yard waste, 4.89% other waste, 2.79% glass waste, 2.16% fabric waste and 1.24% metal. Sungai Penuh City has the capacity to recycle household solid waste is 68.90%. TPS 3R and waste bank was evaluated based on the Technical Guidelines for TPS 3R of The Ministry of Public Works and Housing in 2023 and the Regulation by the Minister of Environment and Forestry Number 14 of 2021. The evaluation results show that 3 units of TPS 3R are in the medium category, 4 units of TPS 3R are in the less category and 9 units of TPS 3R are in the bad category. Meanwhile, waste bank is in the bad category. The potential for waste reduction by TPS 3R and waste bank if operated optimally is 23.26% of the total waste generated in Sungai Penuh City.
Downloads
References
Ozcan, H. K., Guvenc, S. Y., Guvenc,L., & Demir, G. (2016). Municipal solid waste characterization according to different income levels: A case study. Sustainability (Switzerland), 8(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/su8101044
Kementerian PUPR. (2023). Petunjuk Teknis TPS 3R Tempat Pengolahan Sampah 3R.
Wahyono, S., Sahwan, F. L., & Feddy, S. (2013). Pengelolaan Sampah Berbasis Masyarakat Di Rawasari, Kelurahan Cempaka Putih Timur, Jakarta Pusat. Jurnal Teknik Lingkungan, Vol. 13(1), 75–84
Pratama, J. N. (2018). Tata Kelola Sampah di Kota Pekanbaru (Studi Kasus Pada Bank Sampah di Kota Pekanbaru Tahun 2016). Jom Fisip, 5(1), 1–15
Zhang, D., Hao, M., Chen, S., & Morse, S. (2020). Solid waste characterization and recycling potential for a university campus in China. Sustainability, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12083086
Damanhuri, E., & Padmi, T. (2019). Pengelolaan Sampah Terpadu (E. Warsidi (ed.); 2nd ed.). Institut Teknologi Bandung
BPS Kota Sungai Penuh. (2022). Kota Sungai Penuh dalam Angka 2022
Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan. (2021). Peraturan Menteri Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan Republik Indonesia Nomor 14 Tahun 2021 Tentang Pengelolaan Sampah pada Bank Sampah.
Ratri, I. S., Meidiana, C., Eka, K., Jurusan, S., Wilayah, P., & Kota, D. (2022). Peran TPST dan TPS 3R dalam Mereduksi Sampah di Kota Batu. Planning for Urban Region and Environment Journal (PURE), 11(1), 121–132. https://purejournal.ub.ac.id/index.php/pure/article/view/488
Ruslinda, Y., & Indah, S. (2014). Satuan Timbulan, Komposisi dan Karakteristik Sampah Non Domestik Kota Bukittinggi.
Rori, S. V., Rondonuwu, S. G., & Manoppo, F. J. (2022). Optimalisasi Kebutuhan Pengangkutan Sampah dan Potensi Reduksi Timbulan Sampah Dengan Metode Mass Balance di Kecamatan Malalayang Kota Manado. Jurnal Teknik, 20(2), 165–174. https://doi.org/10.37031/jt.v20i2.244
Tonini, D., et al. 2018. Enviromental impacts of food waste: learning and challenge from a case study from UK, Waste Management, 76, pp. 744-766
Fauzi, M., Darnas, Y., Aziz, R., & Chyntia, N. (2022). Analisis Karakteristik dan Potensi Daur Ulang Sampah Non Domestik Kabupaten Solok Selatan sebagai Upaya Meminimalisir Sampah ke TPA. Jurnal Serambi Engineering, 7(4), 3881–3888. https://doi.org/10.32672/jse.v7i4.4835
Putri, A., & Sembiring, E. (2019). Evaluasi Kinerja dan Keberlanjutan Program Bank Sampah sebagai Salah Satu Pendekatan dalam Pengelolaan Sampah dengan Konsep 3R. Jurnal Teknik Lingkungan, 25(18), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.tl.2019.25.1.2
Maryam, A., Raharjo, S., & Aziz, R. (2023). Kajian Aspek Pengolahan Sampah Padang Menggunakan Metode Life Cycle Assessment. Cived, 10(1), 275. https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v10i1.122680
Setiadi, R., Nurhadi, M., & Prihantoro, F. (2020). Idealisme dan Dualisme Daur Ulang Sampah di Indonesia: Studi Kasus Kota Semarang. Jurnal Ilmu Lingkungan, 18(1), 48–57. https://doi.org/10.14710/jil.18.1.48-57
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fitra Rahmadhani, Rizki Aziz, Shinta Indah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







2.jpg)
