Effectiveness of building structure reinforcement to withstand earthquake loads with ETABS V.19 application (Case Study of Commercial Building "Butik Tanah Liek Pusako Mande”)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v11i1.534Keywords:
Commercial Building, Stell Bracing, Story Drift, ETABS V.19Abstract
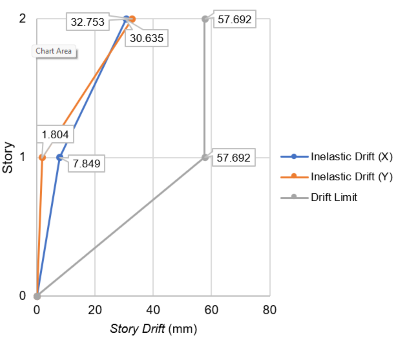
This research addresses the vulnerability of commercial buildings to collapse during earthquakes due to inadequate structural design and identifies the structural weaknesses requiring reinforcement. The focus is on the use of steel bracing as a means to strengthen the structure. The specific case study is the commercial building "Butik Tanah Liek Pusako Mande" in Kota Padang. The research aims to determine whether reinforcing the building with additional steel bracing can enhance its stiffness during seismic events and identify the most effective type of steel bracing. The research methodology employs a quantitative descriptive approach, utilizing structural modeling in analysis software such as ETABS. The study involves analyzing displacements in buildings with and without steel bracing to quantify the effectiveness of the reinforcement. The results indicate that structures employing inverted V bracing achieve a maximum displacement of 9.515 mm in the X direction and 2.525 mm in the Y direction, resulting in a 67% reduction in drift for the X direction and 92% for the Y direction. In contrast, structures using X bracing show a maximum displacement of 30.635 mm in the X direction and 32.753 mm in the Y direction, indicating a 26% increase in drift for the X direction and 36% for the Y direction. The study concludes that inverted V bracing is more effective in reducing building drift compared to X bracing. In conclusion, the research findings suggest that commercial building "Butik Tanah Liek Pusako Mande" already possesses a structural stiffness compliant with standards. However, the addition of inverted V bracing proves effective in further reducing story drift, emphasizing its efficacy in enhancing the structural integrity of commercial buildings during seismic events.
Downloads
References
SNI-1726-2019, Tata Cara Perencanaan Ketahanan Gempa Untuk Struktur Bangunan Gedung dan Nongedung. 2019.
D. Hermon, Geografi Bencana Alam. 2015.
E. Juliafad and H. Gokon, “Study on The Environmental System towards The Development of Assessment Tools for Disaster Reduction of Reinforced Concrete Building due to Future Mega-Earthquake in Padang City, Indonesia,” 2017, doi: 10.11188/seisankenkyu.69.351.
M. I. Sembiring, “EVALUASI KERUSAKAN SOFT STORY PADA STRUKTUR RUMAH TOKO AKIBAT GEMPA (Studi Kasus),” 2022.
L. T. Guevara-Perez, “‘Soft Story’ and ‘Weak Story’ in Earthquake Resistant Design: A Multidisciplinary Approach,” 2012.
S. Matiyas, N. Workeluel, T. Mohanty, and P. Saha, “Review of different analysis and strengthening techniques of soft story buildings,” Mater Today Proc, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2023.04.231.
D. Felli Rahmawati, U. Khatulistiani, M. Program Studi Teknik Sipil, and D. Program Fakultas Teknik Sipil, “ANALISA DRIFT GEDUNG STRUKTUR BAJA TAHAN GEMPA MENGGUNAKAN KOMBINASI TWO STORY-X BRACING DAN X BRACING DI SURABAYA,” vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–16, 2019.
J. A. Repadi, J. Sunaryati, and D. R. Thamrin, “ANALISIS KINERJA STRUKTUR BETON BERTULANG DENGAN VARIASI PENEMPATAN BRACING INVERTED V,” 2016.
C. K. Halim et al., “STUDI PENGARUH VARIASI TIPE PENGAKU DIAGONAL PADA STRUKTUR BANGUNAN BAJA BERTINGKAT TERHADAP PERPINDAHAN LATERAL,” 2020.
PUPR & RSA Ciptakarya, “Desain Spektra Indonesia.” Accessed: Aug. 07, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://rsa.ciptakarya.pu.go.id/2021/index.php?pga=0.7172&ss=1.1245&s1=0.5737&tl=20&kelas=3&range=6#grafik
M. A. Kutuk and I. Gov, “Optimum bracing design under wind loads by using topology optimization,” Wind and Structures, An International Journal, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 497–510, 2014, doi: 10.12989/was.2014.18.5.497.
M. A. Youssef, H. Ghaffarzadeh, and M. Nehdi, “Seismic performance of RC frames with concentric internal steel bracing,” Eng Struct, vol. 29, no. 7, pp. 1561–1568, Jul. 2007, doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2006.08.027.
R. McCaffrey, “The tectonic framework of the sumatran subduction zone,” Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, vol. 37. pp. 345–366, May 2009. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.031208.100212.
D. P. Utomo and B. Purba, “Penerapan Datamining pada Data Gempa Bumi Terhadap Potensi Tsunami di Indonesia,” 2019.
AISC, Seismic Provisions for Structural Steel Buildings. 2010.
F. Hejazi, S. Jilani, J. Noorzaei, C. Y. Chieng, M. S. Jaafar, and A. A. Abang Ali, “Effect of soft story on structural response of high rise buildings,” in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2011. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/17/1/012034.
SNI-1729-2015, Spesifikasi untuk bangunan gedung baja struktural Badan Standardisasi Nasional. 2015. [Online]. Available: www.bsn.go.id
A. M. Nur, “GEMPA BUMI, TSUNAMI DAN MITIGASINYA,” Jurnal Geografi, vol. Vol. 7 No. 1, pp. 66–73, 2010.
A. F. C. Dya and A. W. C. Oretaa, “Seismic vulnerability assessment of soft story irregular buildings using pushover analysis,” in Procedia Engineering, Elsevier Ltd, 2015, pp. 925–932. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.11.103.
SNI-1727-2020, Beban desain minimum dan kriteria terkait untuk bangunan gedung dan struktur lain. 2020.
M. Abidi and M. N. Madhuri, “Review on Shear Wall for Soft Story High-Rise Buildings,” 2012. [Online]. Available: https://hal.science/hal-02494700
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Juniman Silalahi, Raudatul Fitri Jolandina, Fajri Yusmar, Nurhasan Syah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

