Fireless Brick Making using Water Treatment Sewage Sludge with MICP Action
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v10i3.327Keywords:
Brick Sludge, Compressive Strength, Bacillus Subtilis, MICPAbstract
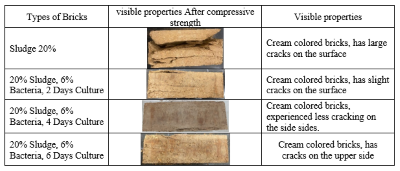
Bricks materials used in making the walls of building. Currently, brick making has new innovations. As in this study using water treatment sludge waste and bacillus subtilis bacteria. Sludge waste done with percentage of 20% and bacillus subtilis bacteria much as 6%. The process adding bacteria called the Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP) process. The process to increase compressive strength clay soil. The purpose study to determine effect of Bacillus subtilis bacteria on the strength bricks using mud and the strength of bricks with bacterial reinforcement. The results showed the compressive strength did not the specifications, where value of the compressive strength of bricks in accordance with SNI 15-2094-2000 is 50 kg / cm². And results of compressive strength only amounted to 22.82 kg / cm² in the 28-day curing period. For compressive strength using mixture of bacteria produces highest strength value the 4-day culture period of 28.11 kg kg/cm².
Downloads
References
H. S. M. D. Isna Apriani, “Pemanfaatan Limbah Lumpur PDAM Gunung Poteng Kota Singkawang Sebagai Bahan Pengganti Tanah Liat Pada,” Jurnal Ilmu Lingkungan, vol. 21, no. 1, p. 22, 2023.
A. Lim, D. A. Muhammad, and A. S. Lestari, “Studi Eksperimental Kemampuan Biosementasi Bakteri Lokal pada Tanah Pasir Lepas,” Jurnal Teknik Sipil, vol. 26, no. 2, p. 129, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.5614/jts.2019.26.2.5.
A. A. Nasser, N. M. Sorour, M. A. Saafan, and R. N. Abbas, “Microbially-Induced-Calcite-Precipitation (MICP): A biotechnological approach to enhance the durability of concrete using Bacillus pasteurii and Bacillus sphaericus,” Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 7, Jul. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09879.
F. Syarif, G. Mahadika Davino, and M. Ferry Ardianto, “Penerapan Teknik Biocementation Oleh Bacillus Subtilis dan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Permeabilitas Pada Tanah Organik Applicability of Biocementation Technique by Bacilus Subtilis and Its Effect of Permeability in Organic Soil,” Jurnal Saintis, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 47, 2020, doi: 10.25299/saintis2020.vol20(01).4809.
Z. D. E. Y. Nevita Elisa, “Sifat Mekanik Beton Dengan Menambah Bakteri Bacillus Subtilis Untuk Aplikasi Beton Pulih Mandiri,” Jom FTEKNIK, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 1–6, 2018.
A. M. Indriani, T. Harianto, A. R. Djamaluddin, and A. Arsyad, “Bioremediation Of Coal Contaminated Soil As The Road Foundations Layer,” International Journal of GEOMATE, vol. 21, no. 84, pp. 76–84, Aug. 2021, doi: 10.21660/2021.84.j2124.
“Badan Standarisasi Nasional Indonesia, (1990), SNI 03-1964-1990, MethodPengujian Berat Jenis Tanah, Jakarta.”.
P. D. D. Mirah Widiastiti, “Analisis Potensi Beberapa Larutan Pengencer Pada Uji Antibakteri Teh Temu Putih,” Jurnal Media Ilmiah Teknologi Pangan, vol. 6, no. 2, p. 117, 2019.
R. S. H. M. Revo Sedrian Putra, “Analisis Kuat Tekan Dan Workability Bata Ringan Cellular Lightweight Concrete Dengan Bahan Tambah Substitusi Semen,” Journal Of Infrastructure And Civil Engineering, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 34–46, 2022.
A. Marini Indriani, G. Utomo, and N. Fitriyani, “Pengaruh Kultur Bakteri Pada Proses Biosementasi Tanah Laterit Terhadap Nilai CBR,” 2023.
R. Agustin, “Kuat Tekan Bata Merah Dengan Variasi Usia Dan Kadar Air Adukan Tanah Liat,” Jurnal Inersia Oktober, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 49, 2016.
H. Prayuda, E. A. Setyawan, and F. Saleh, “Analisis Sifat Fisik dan Mekanik Batu Bata Merah Di Yogyakarta (Analysis Physical And Mechanical Attributes Of Masonry In Yogyakarta),” Jurnal Riset Rekayasa Sipil, vol. 1, no. 2, 2018.
S. E. Sucahyo, A. Firdaus, L. Prodi, T. Lingkungan, A. T. Tirta, and W. Magelang, “Pengelolaan dan Pemanfaatan Limbah Lumpur PDAM Cilacap,”Jurnal Georafflesia, vol. 3, no. 2, p. 81, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://journals.unihaz.ac.id/index.php/georafflesia
American Society For Testing And Materials, “ASTM Standard, (1998), ASTM D 2216-98, Standard Test Method for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil, Rock, and Soil Agregate Mixtures,” ASTM International, 2002.
A. Marini Indriani, G. Utomo, and R. S. Syahputra, “Pengaruh Siklus Basah Kering terhadap Perilaku Mekanik Tanah Lempung Stabilisasi Biosementasi dengan Bakteri Bacillus Subtilis,” Journal Of Civil Engineering And Vocational Education, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 2622–6774, 2023, doi: 10.24036/cived.v10i2.123404.
Iffah Fadliah, “Studi Eksperimental Stabilisasi Biogrouting Bacillus Subtilis Pada Tanah Lempung Kepasiran,” 2013.
H. D. R. Setyanto Iswan, “Studi Kekuatan Batu Bata Pasca Pembakaran Dengan Menggunakan Bahan Additive Serbuk Gergaji Kayu,” Jurnal Rekayasa, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 120–128, 2015.
R. Agustin, “KUAT TEKAN BATA MERAH DENGAN VARIASI USIA DAN KADAR AIR ADUKAN TANAH LIAT,” Jurnal Inersia Oktober, vol. 8, no. 2, p. 49, 2016.
Y. M. P. B. S. Muhammad Saleh Nasution, “Penurunan Permabilitas dan Peningkatan Kuat Geser Tanah Lanau Menggunakan Pengaruh Mikrobakteri Bacillus Subtilis dan Pseudomonas SP,” Jurnal Matriks Teknik Sipil, 2017.
H. Prayuda, H. Nursyahid, and F. Saleh, “Analisis Sifat Fisik Dan Mekanik Bata Beton Di Yogyakarta,” Rekayasa Sipil, vol. 6, pp. 29–40, 2017.
M. P. I. Irna Firnanda and M. Purwandito, “Analisis Kuat Tekan Dan Daya Serap Air Batu Bata Pasca Pembakaran Menggunakan Bahan Campuran Abu Serbuk Kayu,” 2020.
Matsyuri Ayat, “Pengaruh Penambahan Abu Sekam Padi Pada Pembuatan Batu Bata Terhadap Kuat Tekannya,” 2020.
R. Rachmat Syahputra, “Perbaikan Kuat Tekan Tanah Gambut Dari Kabupaten Siak Menggunakan Metode Microbially Induce Calcite Precipitation,” 2021.
Dikky Hilam Maulana, “Pengaruh Penambahan Fly Ash Terhadap Densitas Bata Ringan,” 2023.
M. S. A. Elianora, “Variasi Tanah Lempung, Tanah Lanau Dan Pasir Sebagai Bahan Campuran Batu Bata,” Jurnal Teknobiologi, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 34–46, 2010.
X. Zhang, A. Al-Dossary, M. Hussain, P. Setlow, and J. Li, “Applications of bacillus subtilis spores in biotechnology and advanced materials,” Appl Environ Microbiol, vol. 86, no. 17, Sep. 2020, doi: 10.1128/AEM.01096-20.
J. Yin, J. X. Wu, K. Zhang, M. A. Shahin, and L. Cheng, “Comparison between MICP-Based Bio-Cementation Versus Traditional Portland Cementation for Oil-Contaminated Soil Stabilisation,” Sustainability (Switzerland), vol. 15, no. 1, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.3390/su15010434.
Ekrem Kalkan, “A Review On The Microbial Induced Carbonate Precipitation (MICP) For Soil Stabilization,” International Journal Of Earth Sciences Knowledge And Applications, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 38–47, 2020.
A. M. Indriani and G. Utomo, “Pengaruh Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP) terhadap Perilaku Kuat Geser Tanah Terkontaminasi Batubara,” CIVED, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 53, Mar. 2023, doi: 10.24036/cived.v10i1.122318.
A. M. Indriani, G. Utomo, and H. Ryka, “The Effect Of Microbially Induced Calcite Precipitation (MICP) On Shear Strength Of Coal Contaminated Soil,” 2022.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Evi Ari Ayu Saputri, Andy Marini Indriani, Gunaedy Utomo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







2.jpg)
