Experimental Study of Compressive Strength and Tensile Strength of Foam Mortar with the Addition of Polyethylene Fibers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.24036/cived.v11i1.565Keywords:
Foam Mortar, Compressive Strength, Split Tensile StrengthAbstract
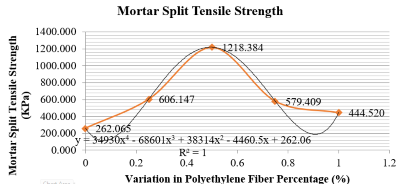
Mortar is a building material of sand, cement, and water that is stirred until homogeneous. So that a light mortar can be obtained, this can be done by mixing the mortar with a foaming agent. Adding polyethylene fiber increases the compressive strength, tensile strength, modulus of elasticity, and brittleness of lightweight mortar. The percentage of added fiber is 0%, 0.25%, 0.5%, 0.75% and 1%. The average density of lightweight mortar added with polyethylene fiber is 895.316 kg/m3. The optimal compressive strength with a fiber ratio of 0.5% polyethylene fiber is 3461.429 kPa, an increase of 172.906% compared to 0% polyethylene fiber. The optimal tensile strength of 0.5% polyethylene fiber is 1218.384 kPa, an increase of 364.917% compared to 0% polyethylene fiber. Based on the results of foam mortar experiments using a foam agent with polyethylene fiber, this is classified as type O mortar, not recommended for interior and exterior walls that do not support structural loads.
Downloads
References
E. Rommel, "Preparation of lightweight concrete from plastic-based artificial aggregates," J. Gamma, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 137-147, 2013.
E. Rahmadona, K. R. Amalia, L. Ulfah, and N. Praditya, "Analysis of Concrete Compressive Strength with Utilization of Silica Fume and Fly Ash as Partial Cement Replacement," Talenta, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 217-223, 2024, doi: 10.33087/talentasipil.v7i1.451.
Warsino, "Effect of Polyethylene Fiber Addition in Gas Technology Lightweight Concrete on Compressive Strength, Split Tensile Strength, and Modulus of Elasticity," J. Tek. Civil, pp. 680-686, 2015.
P. Oktaviani, A. Abrar, and W. Fadli, "Experimental Study of Making Lightweight Bricks by Using Additive Foam Agent," Pros. 2nd Andalas Civ. Eng. Natl. Conf., pp. 139-145, 2015.
A. Susilowati and F. Nabhan, "Effect of Variation of Cement Water Factor on Foam Mortar," J. Appl. Civ. Environ. Eng., vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 9, 2021, doi: 10.31963/jacee.v2i1.2797.
T. Mulyono, Concrete Technology. Yogyakarta: CV. Andi Offset.
D. Mandala Putra and D. Widjaja, "Relationship between split tensile strength and compressive strength of lightweight concrete with crumb rubber and broken roof tiles," Civil Engineering, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 76-88, 2015.
Kardiyono Tjokrodimuljo, Concrete Technology. Yogyakarta: Civil Engineering Publishing Bureau of Civil and Environmental Engineering Student Family UGM, 2007.
S. Farlianti and S. Sapta, "A study of the flexural strength of concrete against the compressive strength of concrete (fc'=25 MPa) using MUSI SUNGAI SAND," Tech. J. Tech., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 79, 2019, doi: 10.35449/teknika.v6i1.106.
S. 03-1971-1990, Test Method for Aggregate Moisture Content. Decree of the Minister of Public Works 1990.
SNI 03-4804-1998, "SNI 03-4804-1998 (Aggregate Content Weight)," Sni 03-4804-1998, pp. 1-6, 1998.
SNI 03-6825-2002, Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cement Mortar. Decree of the Minister of Public Works, 2002.
SNI 03-6882-2014, Specification for Mortar for Pair Unit Work Mortar for Pair Unit Work. National Standardization Agency, 2014.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Rio Marpen, Amiruddin Amiruddin, Efrilia Rahmadona, Indah Islamiati, Yusni Septiani Labais

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







2.jpg)
